Content
What’s the first thing that comes to your mind when you hear the words time expressions? Do you want to learn more about these expressions? Let’s read more about them.
In this lesson, you will be using the time expressions used in both the present simple and continuous tenses.
Remember that:
- The present simple is used to express daily life actions.
- The present continuous is used to talk about actions in progress
Check out other uses for the present simple and continuous:
1: Permanent situations

The present simple expresses permanent or long-term situations. e.g. I love classical music.
2: Facts and general truths

It also makes reference to scientific facts or general truths. e.g. Oil paint is more durable and tougher.
3: Habits and routines

The present simple describes regular or repeated actions. e.g. I usually go to the Palace of Fine Arts during summer vacations.
4: Feelings, Opinions and Beliefs

This structure is used to express thoughts, feelings, and impressions. e.g. Frida Kahlo’s painting style is bizarre.
5: Occupations

The present simple is always used to refer to the occupations or professions people do. e.g. Gabriel Orozco is a Mexican artist.
6: Adverbs of Frequency

Adverbs of Frequency describe how regularly an action happens. They are used in the present simple and have the following basic positions:
- Always: The customer is always right.
- Usually: Our soccer team usually practices twice a week.
- frequently: We practice English outside the classroom frequently.
- Often: Do you often speak with your teachers?
- sometimes
- seldom: Voters seldom know that politicians mean what they say.
- Occasionally He ocassionally watches foreign films.
- Rarely: They rarely go to the library; only when they really need it.
- hardly ever: The students in my class hardly ever participate.
- Never: Tom is never late for school.
- After verb TO BE e.g. Frida Kahlo usually uses vibrant colors in her paintings.
- Before any other verb EXCEPT verb TO BE e.g. I normally work in my study on Saturdays.
- After auxiliary verbs (in affirmative or negative) e.g. I can sometimes take really good photographs.
- At the beginning of a sentence to make emphasis. e.g. Sometimes, we go to art galleries in the city.
Besides using frequency adverbs in Simple Present, we can also use time expressions for this tense.
Remember that time expressions, in general, are short phrases that tell us WHEN, in a timeline, an action happens.In the case of Simple Present, they tell us the frequency with which you do something.
Time Expressions, in any tense can only have 2 positions: at the VERY END of a sentence or at the VERY BEGINNING followed by a comma (,).
Look at the example below:
I have dancing lessons every Monday and Wednesday.
Every Monday and Wednesday, I have dancing lessons.
Now, check the information related to present continous and the time expressions that belong to this tense:
Events happening now

The present continuous is used to talk about actions happening at the moment of speaking e.g. Don’t disturb the artist, he is working.
Temporary situations

It can also refer to situations which happen during a lapse of time. e.g. I’m taking a sculpture course for beginners this semester. It also makes reference to scientific facts or general truths.
Developing actions

This structure refers to actions which are changing with time. e.g. My drawing is getting better and better.
Irritation

It can describe an exasperating habit if you use ‘always’. e.g. Why are you always criticising my painting?
Time expressions

We use the present continuous with time expressions such as: now, at the moment, at present, today, tonight, this morning/afternoon/evening, this week/month/year & while.
- These time expressions have the following basic positions:
- At the very end of a sentence, that is in the complement. e.g. He is living in an apartment at present.
- At the beginning of a sentence make emphasis. In this position, it MUST be followed by a comma (,). e.g. Right now, we are watching the news on TV.
Now, go over the meaning and some examples of the most common time expressions for the present continuous.
- Now: I’m texting my mum now.
- At the moment: The old man is reading the newspaper at the moment.
- At present: Dolores is taking care of her neighbors’ dogs at present.
- Today: My friends and I are having a picnic today.
- Tonight: We’re going to a concert tonight.
- This morning/afternoon/evening: Tom is studying at home this afternoon.
- This week/month/year: The 2012 class is graduating this year.
- While: The cameraman is filming while the reporter is giving the news.
Reading
Activity 1
Every night is another adventure!
How often do you go to art galleries or museums? Do you think working for a museum could be an interesting job?
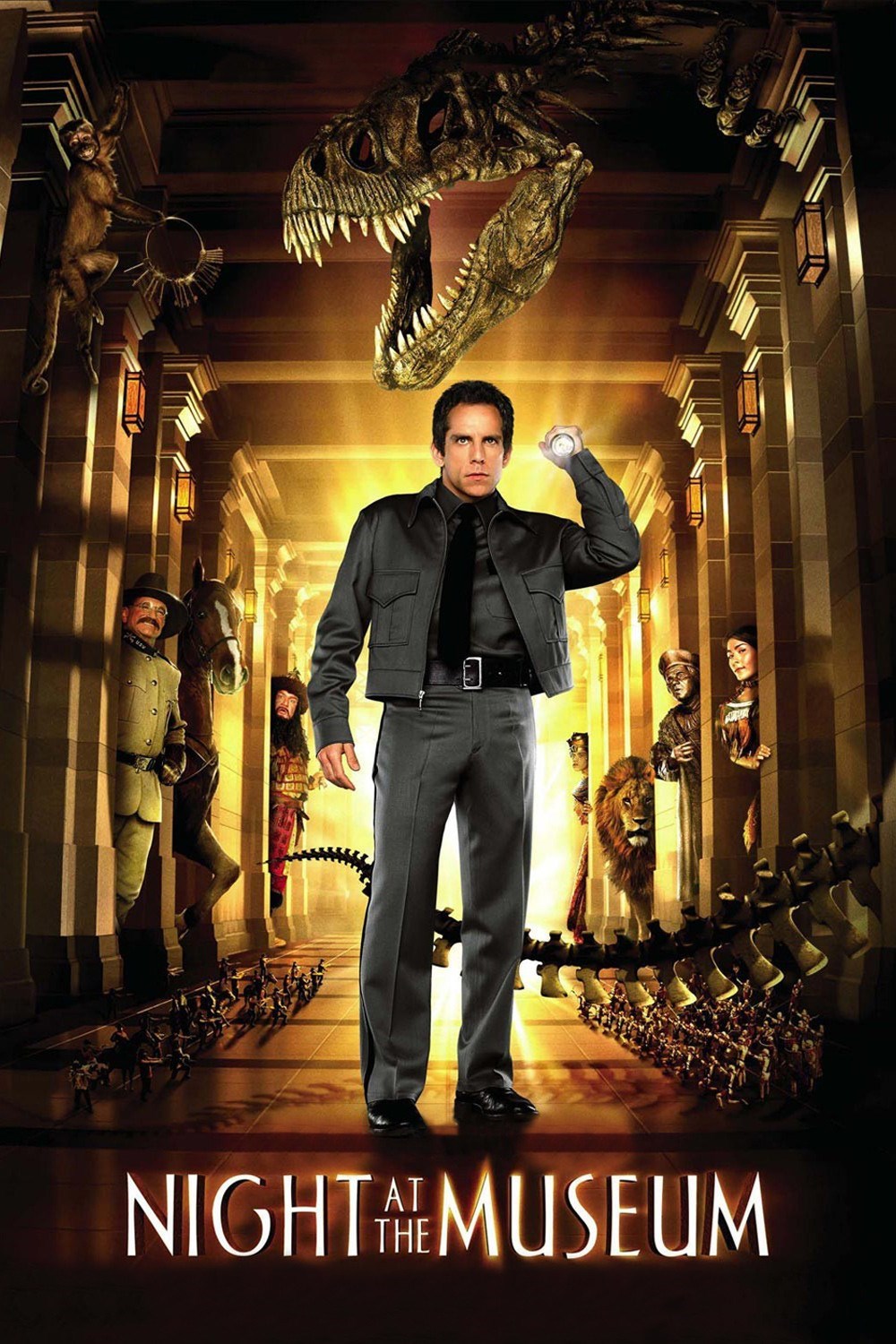
In 2006, 20th Century Fox made a film based on a children's book named: “Night at the Museum” whose main character is a night security guard that works for the American Museum of Natural History. Every night, very strange things happen at the museum and Larry, the museum’s security guard, has to put some order into chaos.
Read the synopsis of the film “Night at the Museum”. Click on thethe Activity to drag the sentences to the appropriate column.
Night at the Museum
Remember to check the elements you need to use in your sentences and answer the questions. Follow the next steps: Click on Activity 1.
Then, check your answers by using the feedback button.
Browse for your file, Click on Upload and finally press the Submit button
Reading
Activity 2
Synopsis
Continue reading about this film and answer the questions about the text.


-
GLOSARY:
- To retire (verb): to stop working, especially because of age or sickness.
- Water fountain (noun): a machine that produces a small stream of water for drinking.
- To go by (phrasal verb): (of time) to pass.
Choose the most appropriate option for the following statements. At the end of the exercise, you will know your score.
Speaking
Activity 3
What about you? What is your day like?
Everybody does many activities with a certain regularity, such as getting up in the morning, taking a shower, having breakfast and going to work or school.
Read about Larry Daley’s daily routine in the following text.
Read about Larry Daley’s daily routine in the following text.
Now, follow the example in Larry’s routine, and record five sentences that give information about your routine that includes the elements below.
- Your occupation
- Time you wake up / take a shower / have breakfast.
- Time you start & finish work/school.
- Three activities you do at school or work.
- Time you arrive home / go to sleep.
The recording should be from 2 to 5 minutes.
Before sending your description, make sure it has the characteristics contained in the rubrics.
Listening
Activity 4
A quick flick!
One day, there is a new exhibit at the Museum of Natural History. It’s a night presentation of the living collections of the museum, but Larry Daley, the security guard, notices that something is going wrong with the museum's characters. It’s the Egyptian stone tablet!
Now, watch the trailer for: “Night at the Museum: Secret of the Tomb” in the link provided.
Choose the sentence that best paraphrases the idea given in each case.
Writing
Activity 5
Let’s go to the Museum
Visiting museums and galleries is fun because you get to learn a lot about art.
First, take a virtual tour of the Tate Modern in London and the Museum of Modern Art (MoMA) in New York City. Follow the steps:
-
1
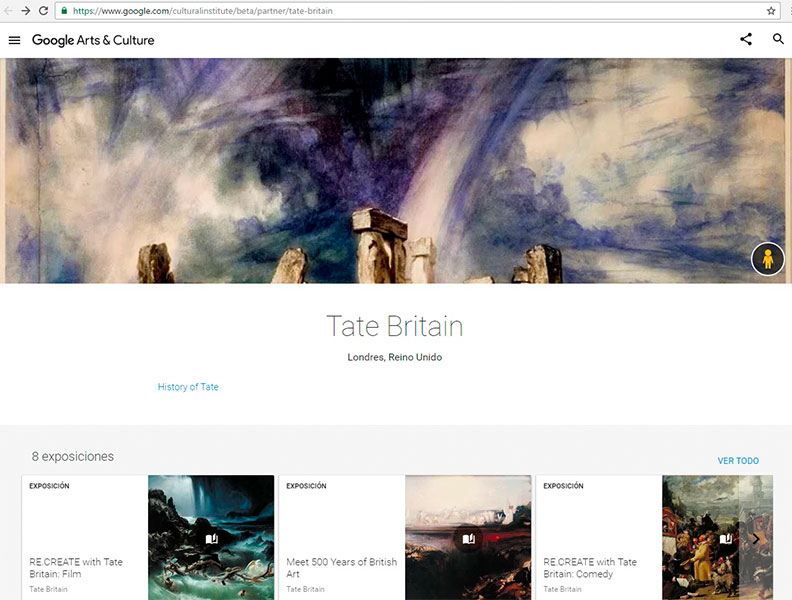
Go to the Tate Modern in London website.
-
2
Now, click in the icon that looks like a man.
-
3
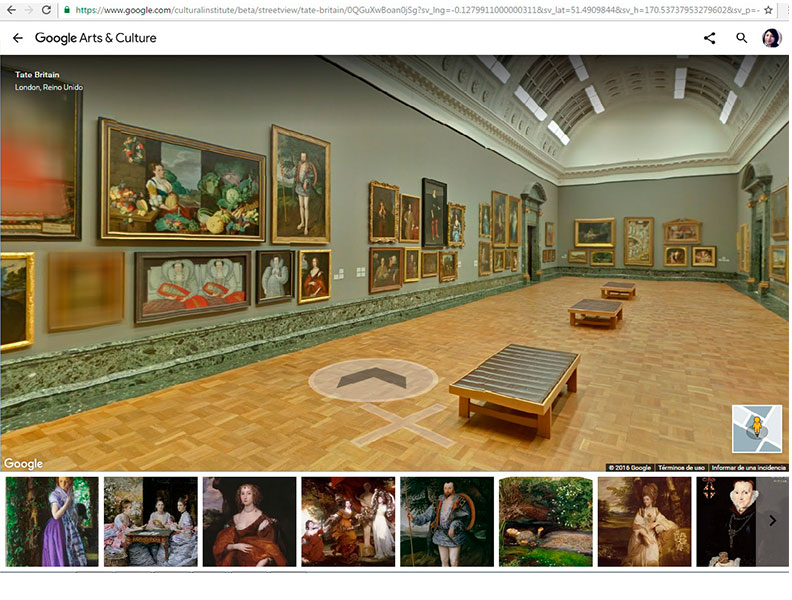
Now you are inside, go around and begin your online tour.
-
4
Go to the Museum of Modern Art website.
-
5
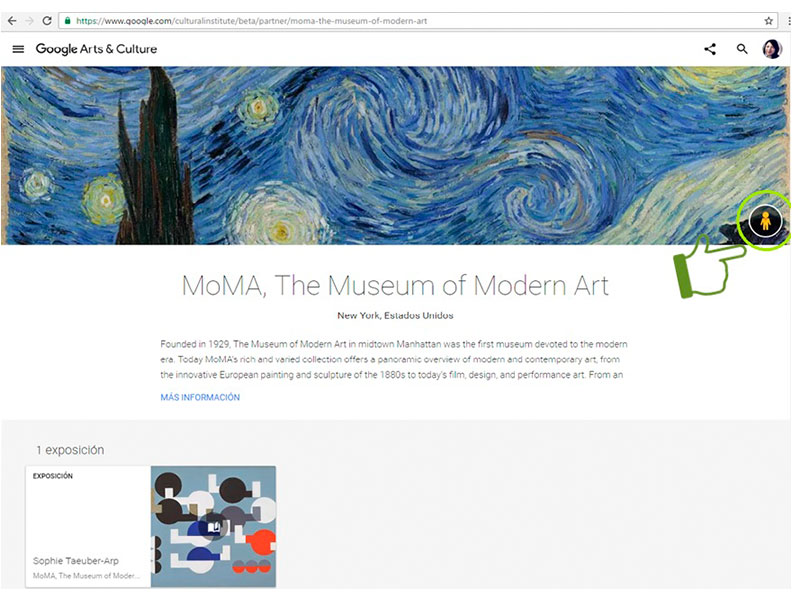
Now, click in the icon that looks like a man.
-
6
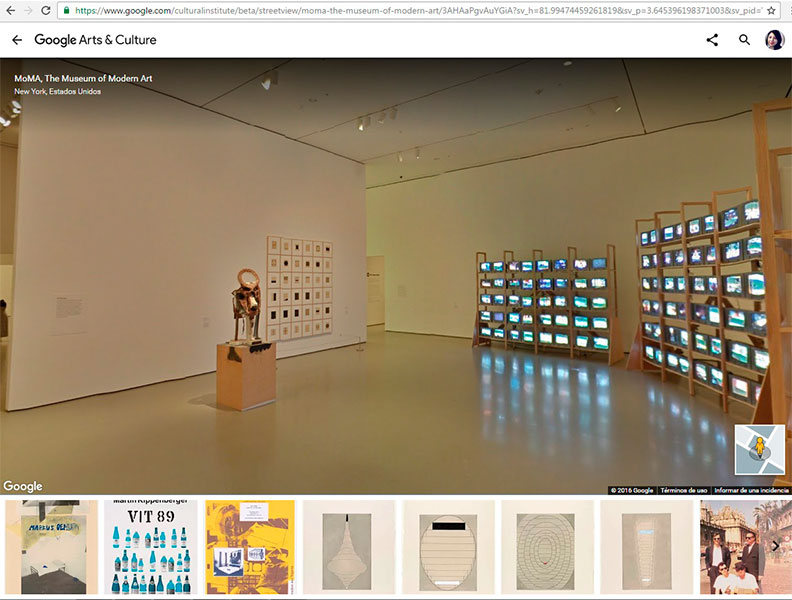
Finally, enjoy your tour around this gallery.
Choose a painting from each gallery and write a 60-word paragraph describing it. Use at least 5 of the eight time expressions below.
- now
- at the moment
- at present
- today
- tonight
- this morning/afternoon/evening
- this week/month/year
- while
Follow the example and the guidelines below:
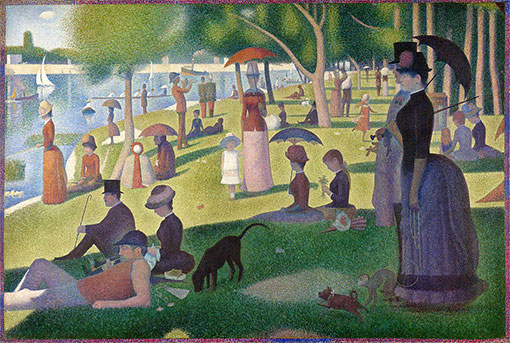
NA. (2015). A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte [photo]. Retrieved from:https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:A_Sunday_on_La_Grande_Jatte,_Georges_Seurat,_1884.
A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La Grande Jatte
This painting represents a big summer day in a park in Paris. On this afternoon, there are many people in the park. They are having picnics at the moment. Some people are watching small sailboats on the water while others are walking around the place. The people are wealthy and are wearing beautiful clothes today. The women are wearing dresses and hats. Many of them are carrying an umbrella while others are sitting under the shades of the trees to protect themselves from the sun.
Remember to check the rubric.




